No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
''Example: “Assess soil and substructure suitability”'' | ''Example: “Assess soil and substructure suitability”'' | ||
<br><br> | |||
[[File: CMG_Hierarchy_1.png]] | [[File: CMG_Hierarchy_1.png]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
'''The number of levels depends on the size of your organisation''' | '''The number of levels depends on the size of your organisation''' | ||
Large enterprises typically have “business areas”, which means that four levels are often apropriate. Most smaller enterprises can be modeled with the other three levels only. | Large [[enterprises]] typically have “business areas”, which means that four levels are often apropriate. Most smaller [[enterprises]] can be modeled with the other three levels only. | ||
'''Focus on specific capabilities (level 4) when designing potential future-state options''' | '''Focus on specific [[capabilities]] (level 4) when designing potential future-state options''' | ||
While levels 1-3 are more for the enterprise-wide, strategic view, specific capabilities are needed to discuss and design the future state in concrete design challenges | While levels 1-3 are more for the [[enterprise]]-wide, strategic view, specific [[capabilities]] are needed to discuss and design the future state in concrete design challenges | ||
'''Size recommendations''' | '''Size recommendations''' | ||
tbd | tbd | ||
Revision as of 09:19, 2 September 2025
Capability Modeling Guidelines | How to Structure a Capability Map
Capability Hierarchy
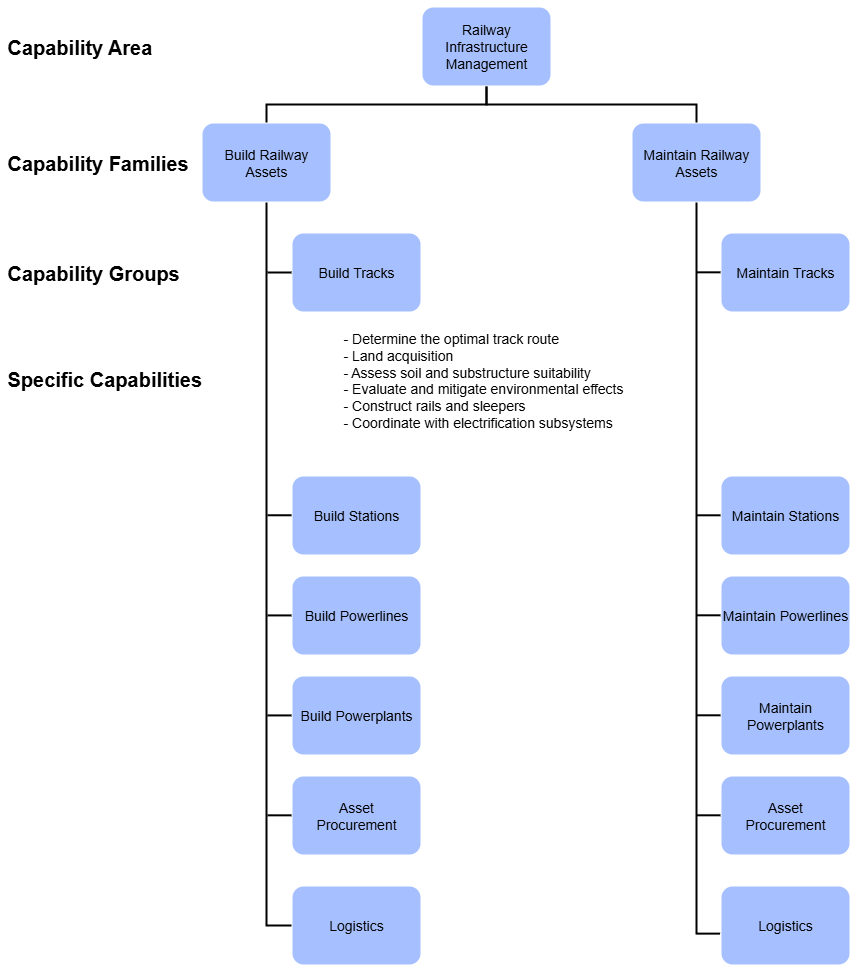
A capability hierarchy is a tree (whole/part relationship) of the enterprise's capabilities, from broad, high-level capabilities at the top (Level 1) to increasingly detailed, granular sub-capabilities at lower levels (Level 2, Level 3, and so on). Superordinate capabilities represent a whole and subordinates represent its parts. By tracing between the higher, more strategic level to specific capabilities hierarchies encourage iteration while supporting coarse to granular assessment of performance. This is essential in making strategy actionable.
EDGY suggests the following levels:
Capability Area:
The highest level represents the major business areas of the enterprise. May not be needed for small enterprises.
Example: “Railway Infrastructure Management”
Capability Family:
Breaks down capability areas into more specific families of capabilities.
Example: “Build Railway Assets”
Capability Group:
Makes capability families more concrete
Example: “Build Tracks”
Specific Capabilities:
Further elaborates on capability groups into very specific capabilities. Here an [[enterprise99 assesses performance, makes sourcing decisions, and addresses gaps.
Example: “Assess soil and substructure suitability”
Practical Tips
The number of levels depends on the size of your organisation
Large enterprises typically have “business areas”, which means that four levels are often apropriate. Most smaller enterprises can be modeled with the other three levels only.
Focus on specific capabilities (level 4) when designing potential future-state options
While levels 1-3 are more for the enterprise-wide, strategic view, specific capabilities are needed to discuss and design the future state in concrete design challenges
Size recommendations
tbd