No edit summary |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<small>[[Enterprise Elements]] | [[Facet and Intersection Elements]] | {{element|Ar Icon-Architecture|Architecture}}</small> | |||
={{element|Ar Element-Asset|Asset}}= | |||
<span class="Ar Def">An object we need and use to perform our capabilities.</span> | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Enterprises need to develop, buy and manage a broad range of tangible | [[Enterprises]] need to develop, buy and manage a broad range of tangible or intangible assets (such as buildings, machines, raw materials, software applications, financial assets and know-how) to perform the [[capabilities]] needed to run their business. Assets as a concept are rooted in economics, strategic management and finance. Buying assets from suppliers connects the enterprise to its supply chain. | ||
or intangible assets (such as buildings, machines, raw materials, | |||
software applications and know-how) to perform the capabilities needed | ==Asset Map== | ||
to run their business. Assets are | |||
strategic management and | [[File:EDGY-Asset-Map.png|EDGY Asset Map / Application Architecture]] | ||
suppliers connects the enterprise to its supply chain. | |||
Depicting [[link]] relationships. Also known as [[Application]] Architecture. | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| Line 18: | Line 21: | ||
==Use== | ==Use== | ||
*Build new capabilities from existing assets. | *Build new [[capabilities]] from existing assets. | ||
*Know your existing assets and build up new ones to improve capabilities | *Know your existing assets and build up new ones to improve capabilities. | ||
*Measure the cost of running a process | *Measure the cost of running a [[process]] by summing up the costs of required assets. | ||
*Manage the procurement and logistics of assets. | *Manage the procurement and logistics of assets. | ||
*Store data in applications that can later be used as an asset in a capability. | *Store [[data]] in [[applications]] that can later be used as an asset in a capability. | ||
* | |||
==Base element== | |||
*{{element|Ar Element-Asset|asset}} is an {{element|Element-Object|object}} | |||
==Related== | ==Related== | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Ar Element-Process|process}} requires {{element|Ar Element-Asset|asset}} | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Ar Element-Capability|capability}} requires {{element|Ar Element-Asset|asset}} | ||
==Suggested Labels== | |||
*material, machine, document, [[application]], [[data]], [[system software]] ([[tagging|tag]]) | |||
*owned, external ([[tagging|tag]]) | |||
*expiry ([[metric]]) | |||
*cost ([[metric]]) | |||
== | {{#seo: | ||
|keywords=EDGY Asset Map,Application Architecture,Enterprise Architecture,Enterprise Application Architecture | |||
|description=In EDGY, an asset is an object we need and use to perform our capabilities. EDGY is Intersection Group's Open Source tool for collaborative Enterprise Design. | |||
|image=EDGY-Asset-Map.png | |||
|image_alt=EDGY Asset Map | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 18:41, 8 June 2023
Enterprise Elements | Facet and Intersection Elements | Architecture
Asset
An object we need and use to perform our capabilities.
Description
Enterprises need to develop, buy and manage a broad range of tangible or intangible assets (such as buildings, machines, raw materials, software applications, financial assets and know-how) to perform the capabilities needed to run their business. Assets as a concept are rooted in economics, strategic management and finance. Buying assets from suppliers connects the enterprise to its supply chain.
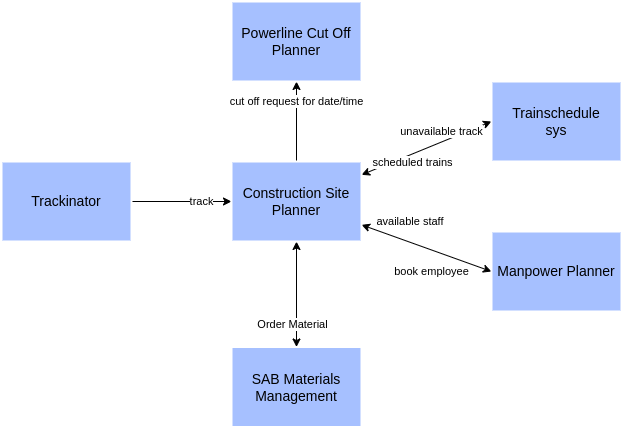
Asset Map
Depicting link relationships. Also known as Application Architecture.
Examples
- A railroad maintenance company requires fuel and gravel, and operates power lines and tracks.
- A freelance legal adviser works with contracts, legal texts and court decisions.
- A public healthcare provider operates with hospital buildings, medical records, and planning systems.
- An air traffic control organisation runs applications and databases to track flights, airlines and airports.
Use
- Build new capabilities from existing assets.
- Know your existing assets and build up new ones to improve capabilities.
- Measure the cost of running a process by summing up the costs of required assets.
- Manage the procurement and logistics of assets.
- Store data in applications that can later be used as an asset in a capability.
Base element
Related
- process requires asset
- capability requires asset
Suggested Labels
- material, machine, document, application, data, system software (tag)
- owned, external (tag)
- expiry (metric)
- cost (metric)