No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
={{element|Or Organisation|Organisation}}= | ={{element|Or Organisation|Organisation}}= | ||
<span class="Or Def">A group of people working together.</span> | |||
Description | ==Description== | ||
An organisation is a complex social structure. People form organisations | An organisation is a complex social structure. [[People]] form organisations to collaborate and co-create [[outcomes]] they cannot achieve alone without explicit agreements about membership, responsibilities and behavioural rules. Organisations are fractal: they are made up of nested structures (e.g. business unit-department-team) that have similar attributes on each level, such as [[purpose]], [[goals]], [[capabilities]] and ''hierarchy''. | ||
to collaborate and co-create outcomes they cannot achieve alone | |||
without explicit agreements about membership, responsibilities and | |||
behavioural rules. Organisations are fractal: they are made up of | |||
nested structures (e.g. business unit-department-team) that have | |||
similar attributes on each level, such as purpose, goals, capabilities and | |||
hierarchy. | |||
Organisations are complex adaptive systems. This means they display | Organisations are complex adaptive systems. This means they display attributes and behaviours that are designed and managed, as well as ''emergent'' attributes and behaviours that arise more or less unplanned out of people's complex behaviour. This emergence means organisations are never fully predictable and deterministic, making organisational design always a mix of design and influence. Organisational aspects that lend themselves best to be designed are organisational structures, roles, responsibilities, formal collaboration and decision-making processes. Aspects that are much harder or impossible to design are organisational culture, responsiveness to unexpected situations, adaptability, resilience and robustness. | ||
attributes and behaviours that are designed and managed, as well as | |||
emergent attributes and behaviours that arise more or less unplanned | ==Organisation Map== | ||
out of people's complex behaviour. This emergence means organisations | |||
are never fully predictable and deterministic, making organisational | [[File:EDGY-Organisation-Map-Org-Chart-Organigram.png]] | ||
design always a mix of design and influence. Organisational aspects that | |||
lend themselves best to be designed are organisational structures, roles, | Also known as Organisational Chart or Organigram. | ||
responsibilities, formal collaboration and decision-making processes. | |||
Aspects that are much harder or impossible to design are organisational | |||
culture, responsiveness to unexpected situations, adaptability, resilience | |||
and robustness. | |||
==Examples== | ==Examples== | ||
| Line 30: | Line 20: | ||
==Use== | ==Use== | ||
*Set up team structures and group people together to realise the capabilities of the enterprise. | *Set up [[team]] structures and group [[people]] together to realise the [[capabilities]] of the enterprise. | ||
*Divide and organise our work into roles and responsibilities. | *Divide and organise our work into roles and responsibilities. | ||
*Define ownership and accountability for enterprise elements. | *Define ownership and accountability for [[enterprise elements]]. | ||
*Establish ways of collaboration and decision-making. | *Establish ways of collaboration and decision-making. | ||
==Base element== | |||
*{{element|Or Organisation|organisation}} is an {{element|Element-Object|object}} | |||
==Related== | ==Related== | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Or Organisation|organisation}} builds {{element|Br Element-Brand|brands}} | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Or Organisation|organisation}} makes {{element|Pr Element-Product|products}} | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Or Organisation|organisation}} pursues {{element|Id Element-Purpose|purposes}} | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Or Organisation|organisation}} authors {{element|Id Element-Story|story}} | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Or Organisation|organisation}} has {{element|Ar Element-Capability|capabilities}} | ||
*{{ | *{{element|Or Organisation|organisation}} performs {{element|Ar Element-Process|processes}} | ||
== | ==Suggested Labels== | ||
* | *company, association, governmental, team, project, informal group, role ([[tagging|tag]]) | ||
* | *hierarchical, matrix, committee, autonomous ([[tagging|tag]]) | ||
* | *internal, shared, external ([[tagging|tag]]) | ||
* | *satisfaction ([[metric]]) | ||
* | *span ([[metric]]) | ||
*cost ([[metric]]) | |||
Revision as of 19:57, 21 March 2023
Organisation
A group of people working together.
Description
An organisation is a complex social structure. People form organisations to collaborate and co-create outcomes they cannot achieve alone without explicit agreements about membership, responsibilities and behavioural rules. Organisations are fractal: they are made up of nested structures (e.g. business unit-department-team) that have similar attributes on each level, such as purpose, goals, capabilities and hierarchy.
Organisations are complex adaptive systems. This means they display attributes and behaviours that are designed and managed, as well as emergent attributes and behaviours that arise more or less unplanned out of people's complex behaviour. This emergence means organisations are never fully predictable and deterministic, making organisational design always a mix of design and influence. Organisational aspects that lend themselves best to be designed are organisational structures, roles, responsibilities, formal collaboration and decision-making processes. Aspects that are much harder or impossible to design are organisational culture, responsiveness to unexpected situations, adaptability, resilience and robustness.
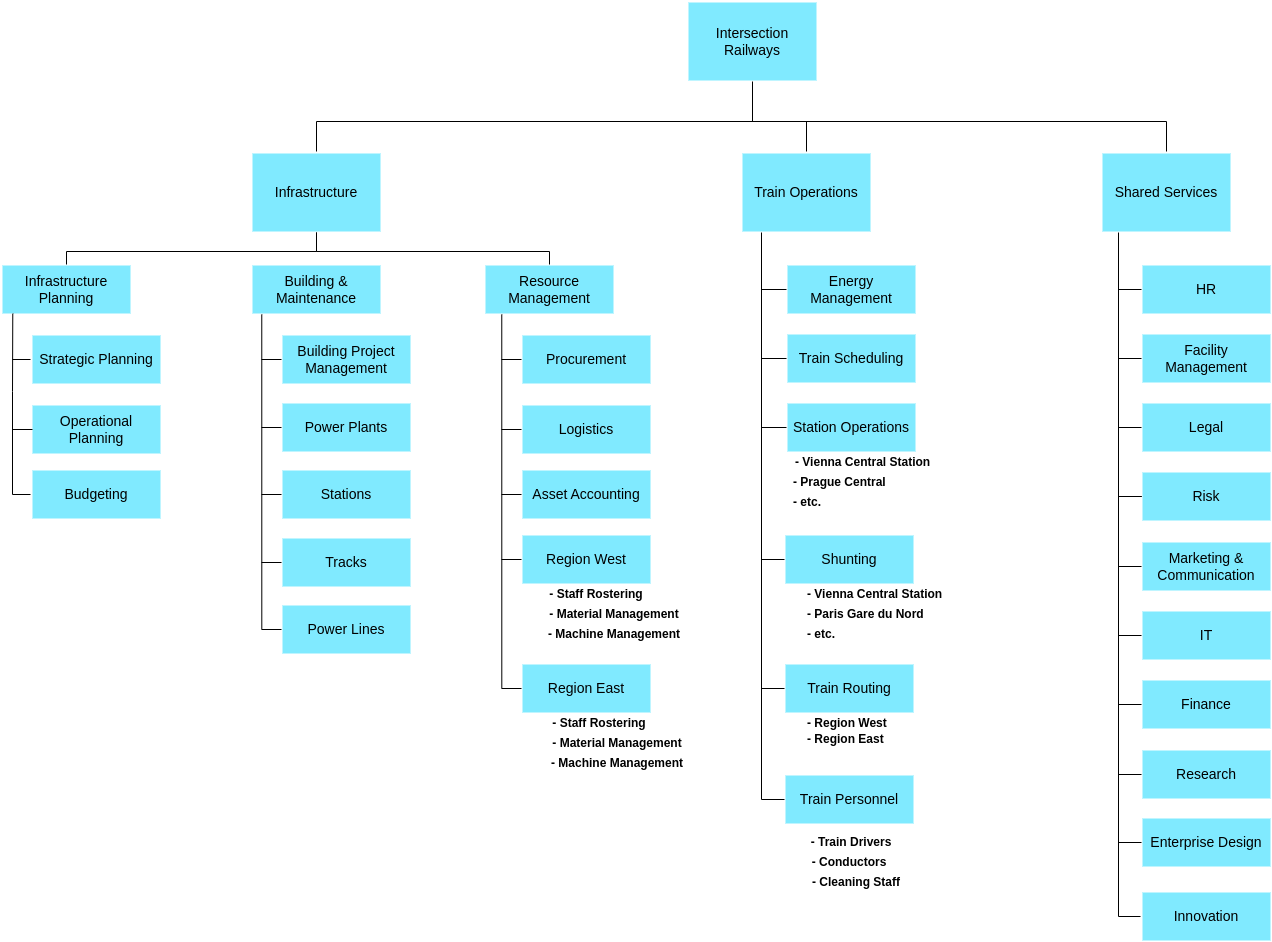
Organisation Map
Also known as Organisational Chart or Organigram.
Examples
- A commercial company is structured into a hierarchy of roles and responsibilities.
- A public service implements decision-making structures needed to manage their organisation's collective performance.
- An NGO defines volunteer roles and processes needed to direct the organisation to maximise its effectiveness and impact.
Use
- Set up team structures and group people together to realise the capabilities of the enterprise.
- Divide and organise our work into roles and responsibilities.
- Define ownership and accountability for enterprise elements.
- Establish ways of collaboration and decision-making.
Base element
- organisation is an object
Related
- organisation builds brands
- organisation makes products
- organisation pursues purposes
- organisation authors story
- organisation has capabilities
- organisation performs processes